The reasons why I consider this scientific article published in 2009 a milestone on this subject are many: the authority of the Authors, the large case series of over 3000 patients, the fact that they also evaluated the mild descent of the cerebellar tonsils (Low-Lying Cerebellar Tonsils) and not only the descent of the cerebellar tonsils sufficient to configure Chiari type I malformation (CM1), and the correlation of the various descents of the cerebellar tonsils with tethered cord syndrome and occult tethered cord syndrome.
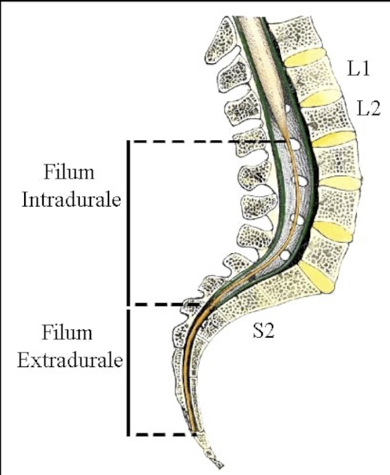
I would like to point out that the surgical treatment of tethered cord syndrome and occult tethered cord syndrome was performed under GENERAL ANESTHESIA with section of the INTRADURAL FILUM TERMINALE.
My minimally invasive surgical procedure under LOCAL ANESTHESIA for the EXTRADURAL section of the FILUM TERMINALE, which I will discuss further here and on other pages of the website, was published later in 2018, although I have been performing it since 2010.
© Copyright 2020 Vanni VERONESI. All rights reserved.
Privacy Notice (ITALIANO) / Privacy Policy (ENGLISH)Cookie Notice (ITALIANO) / Cookies information (ENGLISH)
MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY UNDER LOCAL ANESTHESIA FOR THE SECTION OF THE EXTRADURAL (EXTERNUM) FILUM TERMINALE
Minimally invasive surgery under local anesthesia for the section of the filum terminale of the extradural tract may present as its only complication a skin infection at the site of the surgical incision. To prevent this possibility, the protocol includes antibiotic prophylaxis in the operating room before the procedure.
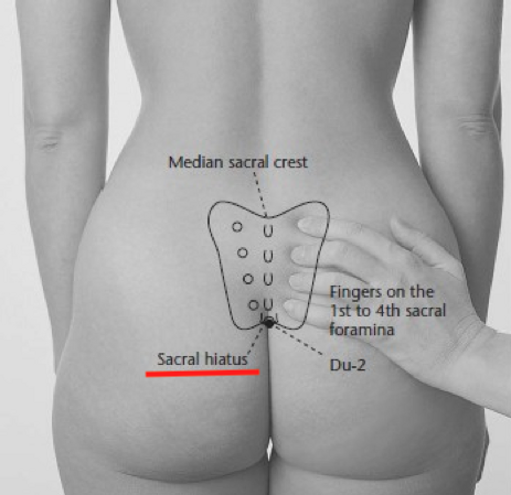
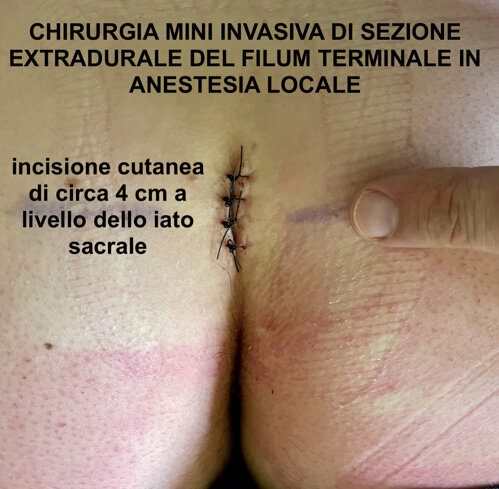
The skin incision measures about 4 cm and is performed at the level of the sacral hiatus. During this procedure, no bone tissue is removed from the vertebrae or the sacrum. Using a microsurgical technique with an operating microscope, the posterior sacrococcygeal ligament is removed and the extradural filum terminale is isolated and cut. For a video description of the technique, CLICK HERE.
Thanks to the absence of meninges or nerve structures in the surgical field, there is no neurological damage or onset of meningitis. The surgical procedure lasts about 25 minutes and the patient can start walking again about 60 minutes later. The patient is discharged from the hospital the same day as the procedure or the following day.
For anatomical reasons, the procedure does not involve opening the meninges. Therefore, this minimally invasive surgical technique, in addition to not having the complications of classic surgery (for a list, see the next post), eliminates the risks of re-tethering due to opening of the meninges typical of traditional surgery under general anesthesia.
- LOCAL ANESTHESIA
- SMALL SKIN INCISION (see box below)
- SHORT DURATION OF THE PROCEDURE
- NO NEUROLOGICAL COMPLICATIONS
- IT IS NOT POSSIBLE TO HAVE MENINGITIS AS A COMPLICATION
- AFTER THE SURGICAL PROCEDURE, ONLY ONE HOUR OF BED REST
- DISCHARGE FROM HOSPITAL ON THE DAY OF SURGERY
- THERE ARE NO ANATOMICAL CONDITIONS FOR RETETHERING
A small skin incision is sufficient to perform the minimally invasive surgical approach to the sacral spinal canal through the sacral hiatus

INFORMATIONAL VIDEO
SECTIONING OF EXTRADURAL FILUM TERMINALE UNDER LOCAL ANESTHESIA:
- ANATOMY
- SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
- POSTOPERATIVE COURSE
FOR SCIENTIFIC AND INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES, CLICK BELOW TO LEAVE THIS WEBSITE AND CONNECT TO THE YOUTUBE CHANNEL OF VERONESI VANNI AND WATCH THE VIDEO

SECTIONING OF EXTRADURAL FILUM TERMINALE EXTERNUM UNDER LOCAL ANESTHESIA
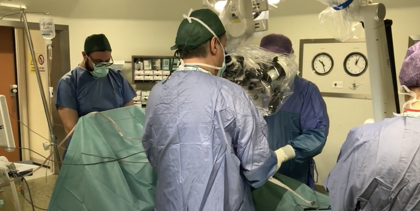
In the video, the Brazilian patient is awake and speaks with the interpreter Prof. Giorgio Charissiadis, who describes the surgical steps to her.
The operating microscope is used in the central part of the surgical procedure for the sectioning of the extradural filum terminale.
SURGICAL VIDEO

TRADITIONAL SURGERY UNDER GENERAL ANESTHESIA FOR THE SECTIONING OF THE INTRADURAL FILUM TERMINALE
Traditional surgery of the intradural section of the filum terminale requires general anesthesia for about one or two hours.
Among the risks of traditional surgery under general anesthesia are included permanent deficits in urinary and fecal sphincter control, new neurological deficits.
Risk of cerebrospinal fluid loss, pseudomeningocele, tethering of the cauda equina, tethering of the medullary cone with possible need for subsequent surgical interventions.
Risk of wound healing problems and meningitis with associated morbidity and mortality.
The traditional surgical approach involves:
- removal of the posterior part of the vertebrae;
- opening of the meninges;
- identification of the intradural filum terminale among the nerve roots of the cauda equina (and verification by means of electrostimulation to avoid cutting the nerve roots with consequent neurological damage).
The duration of the operation is about 60-90 minutes.
Before starting the operation, still under general anesthesia, time is added to prepare intraoperative electrophysiological monitoring.
The length of the skin incision is usually about 8-12 cm.
After surgery, bed rest in the prone position is required for one or two days.
Discharge is expected three or four days after the operation.
With this technique, cases of retethering have been described due to adhesions of the previously opened meninges.
The use of the endoscope reduces the length of the skin incision and invasiveness but does not significantly change the other aspects and complications of the traditional technique.